
For folks suffering from drug addiction, specific cues—whether it truly is distinct people, spots or things—can induce effective cravings for recurring use.
A new University of Michigan research has determined brain alerts, typically related with irritation, contributing to people’s vulnerability to addiction. With repeated drug use with the same exposure to cues, some people establish an lack of ability to management their drug use, even in the deal with of damaging consequences.
The review is printed in the journal eNeuro.
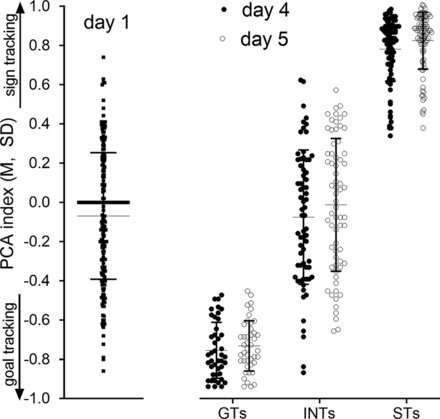
In rats, researchers have shown that animals with lousy attentional control—choosing what is provided focus to and what is ignored—develop potent cue-induced cravings. They are called sign trackers. Animals with very good attentional command are regarded aim trackers.
Hanna Carmon, U-M psychology graduate scholar and the study’s direct writer, mentioned sign trackers expertise a larger rewarding impact of drug using and will proceed to get prescription drugs even when there are distressing effects. Aim trackers prevent drug using in the facial area of outcomes.
Carmon and colleagues targeted on the relationship among the brain’s choline transporter—a protein in the cell membrane concerned in attentional control—and cytokines—proteins that promote or sluggish the immune system—and the variances amongst indicator and target trackers.
In the research, sign trackers had extra choline transporters that are dysfunctional, which contributed to their bad attentional management. They also possessed elevated cytokines.
When scientists induced cytokine concentrations to raise, sign trackers knowledgeable very very little adjust in the variety of choline transporters regarded as dysfunctional having said that, in goal trackers, they noticed an anticipated increase in dysfunctional choline transporters, earning them far more like indicator trackers.
“These results indicate that there is an critical conversation amongst greater cytokine output and lowered choline transporter function that contributes to disrupted attentional control and vulnerability to addiction,” Carmon claimed.
Although it is tricky to exam no matter if human sign trackers are susceptible to habit, in both of those rats and people, indicator trackers exhibit several behaviors that demonstrate very poor attentional regulate, such as distractibility and impulsiveness. Indicator trackers, as a result, symbolize dependancy vulnerability, whereas goal trackers stand for habit resiliency.
As much more analysis is completed in this subject, the study’s authors hope it will lead to much better individualized therapies for those battling with dependancy.
The study’s other authors were psychology university student Evan Haley and Vinay Parikh, associate professor of psychology, both equally of Temple University and U-M’s Natalie Tronson, associate professor of psychology, and Martin Sarter, professor of psychology.
Additional details:
Hanna Carmon et al, Neuro-Immune Modulation of Cholinergic Signaling in an Addiction Vulnerability Trait, eNeuro (2023). DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0023-23.2023
Quotation:
Immune alerts that lead to habit vulnerability identified in the brain (2023, March 21)
retrieved 22 March 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-03-immune-contribute-addiction-vulnerability-brain.html
This document is topic to copyright. Aside from any good dealing for the goal of private study or investigation, no
aspect may perhaps be reproduced without the created authorization. The written content is supplied for information and facts applications only.







